Sponsored
Ubuntu is one of the famous GNU/Linux operating systems. Linux Mint is an operating system derived from Ubuntu and it is now leading in DistroWatch.com. Let us check how to install Ubuntu or Ubuntu-based operating systems like Linux Mint can be installed in your computer. Please read GNU/Linux Checklist if you are going to install along with Windows.
Contents
Download Ubuntu ISO and make it bootable
- Download ISO from official source.
- Make it bootable by writing to a DVD or create a bootable pendrive.
- To create a bootable pendrive from windows you can use Rufus software. It is lightweight and simple to use.
- If you have another GNU/Linux OS already installed you can use Unetbootin for this purpose.
Boot and select Install Ubuntu
- Connect bootable medium (Pendrive/DVD) to computer and boot from it.
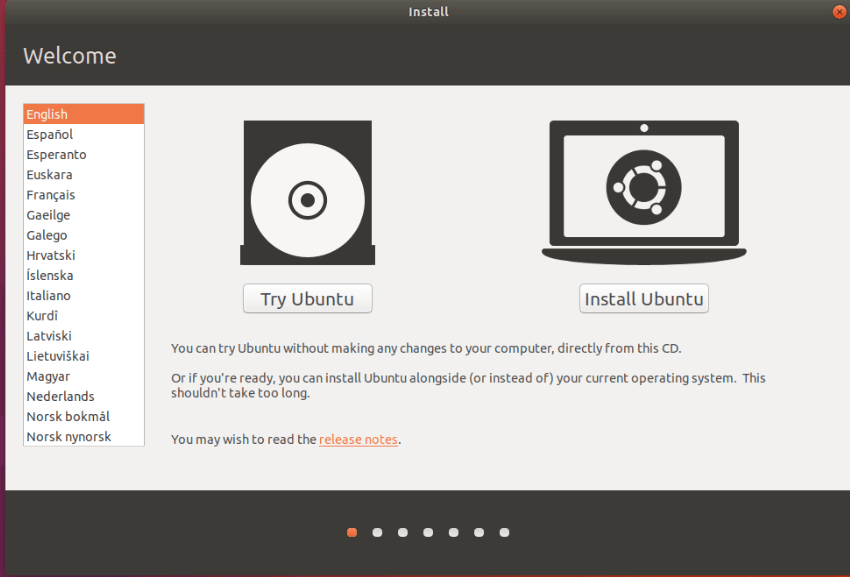
- You will see a window with Try Ubuntu and Install Ubuntu options. The Try Ubuntu option helps you to test Ubuntu without installing to your computer. You can also install and run other applications in this live system.
- Select Install Ubuntu option to continue with installation.
Sponsored
- Check Install third-party softwares if you need non-free driver softwares, codecs, etc.
Prepare hard disk for Installation
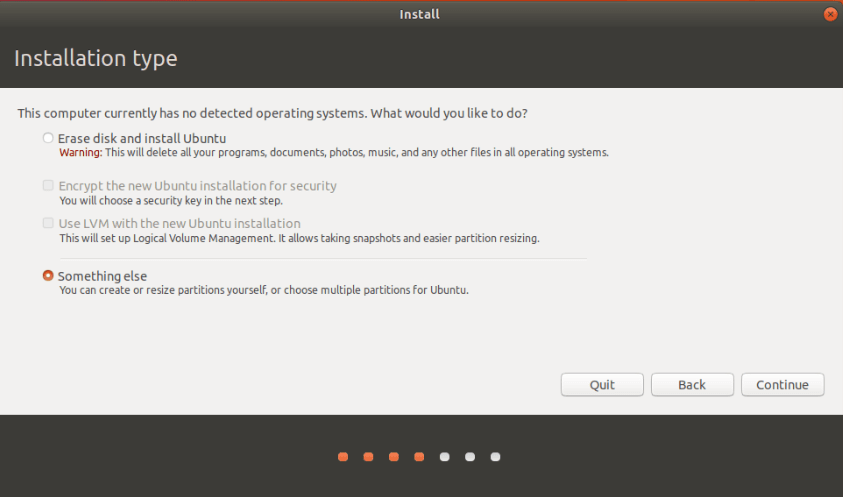
- Then you can see a window like below asking Installation type. If your hard disk contains other operating systems like Windows, it’s better to go with the Something else option. The main options are:
- Erase disk and install Ubuntu
- Install Ubuntu alongside Windows (if Windows already exists in your computer)
- Something else
- If you choose Something else, you can decide how to partition your hard disk. Here we are going with Something else.
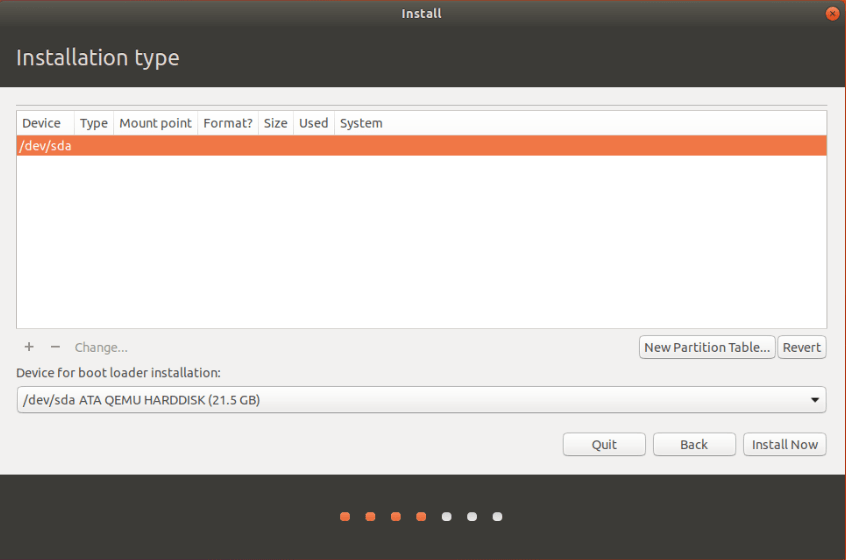
- Now you can see the hard disk partitions and free space available. If Windows is already installed you can see Windows partitions here (FAT32 or NTFS partitions). In this example we are going to use a fresh hard disk. First you need to make a partition table to continue.
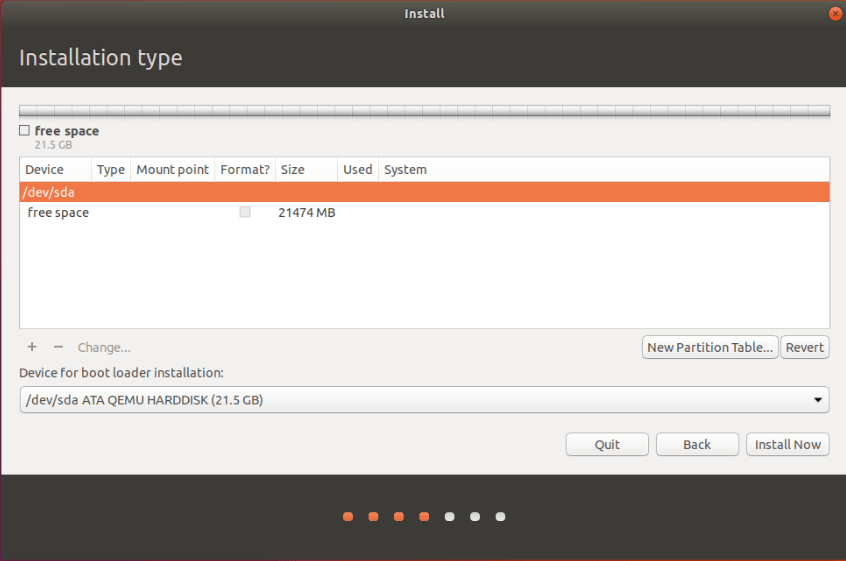
- Now you can see the freespace. We are partitioning with this freespace. If you installed other OS before, make sure to make enough freespace before installing.
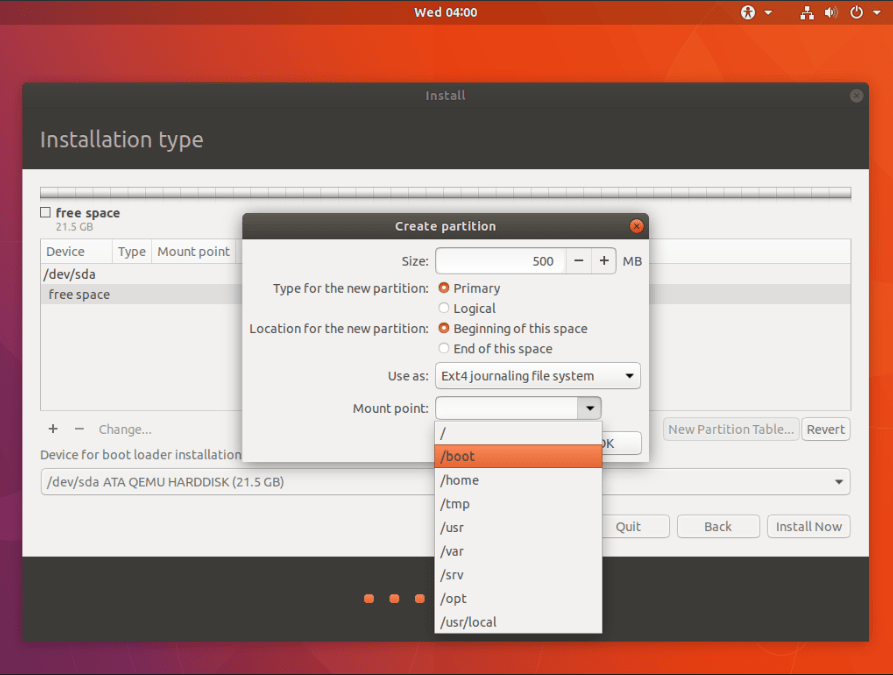
- Let start with partitioning. The required partitions are as follows:
- /boot – 500MB or /efi 100 MB (EFI partition is needed only in UEFI mode installation. If Windows is installed in UEFI then this partition will already be there)

- Swap area – Swap space in Linux is used when the amount of physical memory (RAM) is full. If the system needs more memory resources then this space in hard disk acts as RAM.

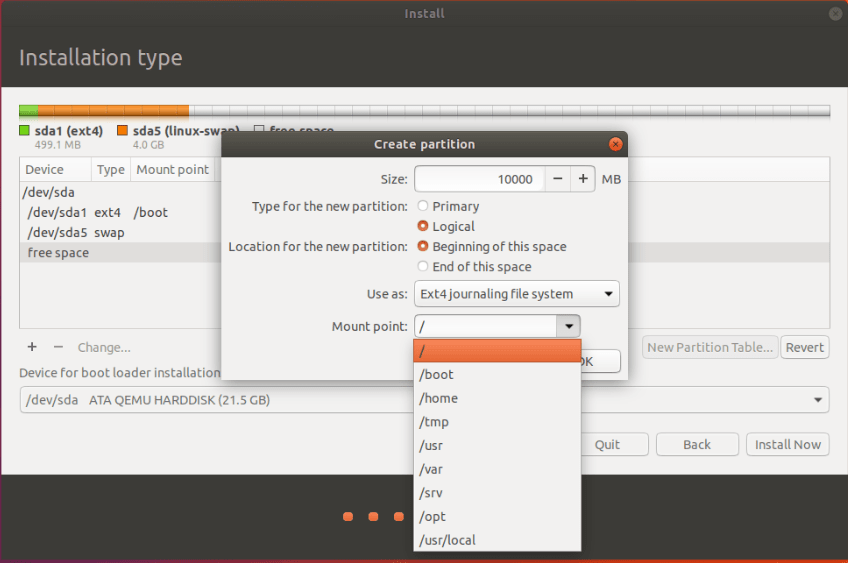
- / – 30 to 50 GB – This is the root area, where operating system is going to be installed.

- /home – You can assign the rest of the hard disk space for this partition. User files (photos, videos, music, etc.) and user-specific configuration files will be stored here.
- /boot – 500MB or /efi 100 MB (EFI partition is needed only in UEFI mode installation. If Windows is installed in UEFI then this partition will already be there)
Note: Select ext4 option in Use as dropdown for all the partitions except for swap. For swap select swap area.
Configure basic settings to Install Ubuntu
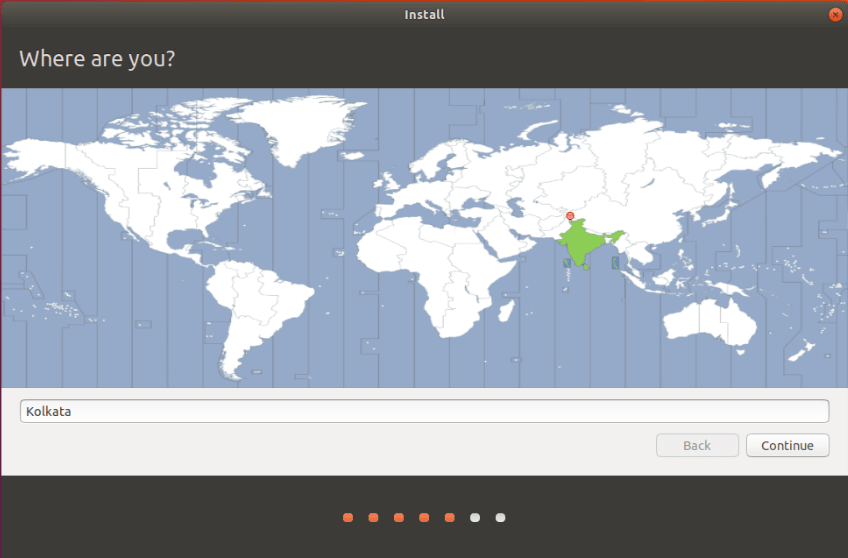
- Select country from the map provided
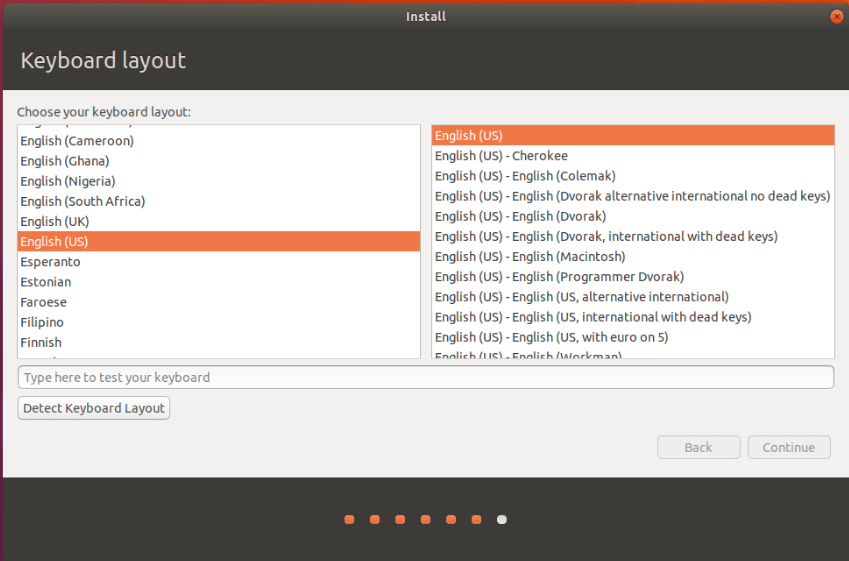
- Select keyboard layout
- Give username and password
Finish Installation
- Press continue. Voila, you are done!
Don’t forget to reboot are remove the live installation media before using Ubuntu.
Sponsored